Application Effect of Soybean Active Dry Yeast in Soy Sauce
Lei Jincheng 1, Chang Yi 1, Song Huanlu 2, Xu Qianqian 2
(1. Angel Yeast Co., Ltd., Brewing and Bio-Energy Division, Institute of Brewing and Bio-Energy, Yichang, 443003; 2. School of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, Beijing Technology and Business University, Beijing, 100037)
Abstract : The application effect of soy sauce yeast in soy sauce production was studied by using headspace-solid phase microextraction (HS-SPME) combined with GC chromatography (GS-MS). The soy sauce yeast was mainly described in terms of aroma. Contribute to reflect the superiority of artificial addition (supplementation) of yeast in the production of soy sauce from the changes in the aroma constituents, ethanol concentration, 4-ethylguaiacol, and 4-ethylphenol.
Keywords: soy sauce production, soy sauce yeast, HS-SPME, GS-MS, flavoring
Soy sauce is one of the most traditional condiments in China. With the continuous development and progress of the soy sauce industry, soy sauce has become more and more common households in all parts of the world. Nowadays, soy sauce has become an important condiment including European and American countries. One 1].
Japanese soy sauce is a typical representative of the world's soy sauce market. Manually adding yeast and lactic acid bacteria is a distinct difference between Japanese soy sauce production and Chinese soy sauce production [2]. Many scholars and factories are committed to making better soy sauce by changing the soy sauce fermentation process and conditions [3-4]. Soy sauce yeast is one of the important sources of soy sauce aroma [5-6]. With regard to the influence of soy sauce yeast on the aroma of soy sauce, many scholars including Japanese scholars have done considerable research on the aroma components of soy sauce[7-8]. The aroma of soy sauce is the result of a complex action, among which soy sauce yeast plays a very important role in the formation of soy sauce aroma [9]. Ethanol produced by the main fermenting yeast of Ruthenium yeast is a precursor of many ester substances, and the 4-methylguaiacol and 4-methylphenol substances produced by the main fermenting yeast of P. source. In addition, soy sauce yeast is also involved in the synthesis of various substances such as sterols, phenylethyl alcohol, glycerol, etc., and has a vital role in the flavor of the final soy sauce brewed product.
1. Materials and Methods
1.1 Experimental Materials
1.1.1 Soy Sauce Samples
The soy sauce samples were taken from six soy sauce factories A, B, C, D, E, and F, respectively. Each factory added yeast according to actual production conditions. All the tested samples had a control sample.
1.1.2 Main reagents
3-Methyl-2-heptanone and n-hexane are chromatographic grades and were purchased from Sigma, USA.
1.1.3 The main instrument
Solid-phase microextraction head: Supelco, Canada; GC6890-MS5975: Agilent, USA.
1.2 Experimental Methods
1.2.1 sample extraction
Before the sample preparation, the SPME extraction fiber head (CAR/PDMS, 75 μm) was firstly aged on the GC inlet, and the aging temperature was 250°C for 30 min.
Take 5g of sample into a 15ml SPME extraction vial and equilibrate for 30min at 50°C. Then the SPME extraction needle was inserted into the headspace of the extraction vial for 40 min.
1.2.2 Sample Detection
After the adsorption was completed, the extraction head was quickly removed and inserted into the GC inlet. The extraction head was heated at the injection port for 10 min.
The programmed temperature, mass spectrometry, and GC-O conditions of the gas chromatography are as follows:
After the sample is injected, it is separated by a capillary column of a meteorological column and then split in a ratio of 1:1:1. The separated sample enters a gas chromatographic FID detector, a mass spectrometer detector (MSD), and a olfactory port (ODP). The sample enters three detectors at the same time, which reduces the experimental analysis error.
The temperature of the GC program was: the initial temperature was 40° C., kept for 3 min, increased to 200° C. at 5° C./min, held for 0 min, and then raised to 260° C. at 15° C./min for 3 min.
The electron mass spectrometry was EI, the electron energy was 70 eV, the ion source temperature was 230°C, and the quadrupole rod temperature was 150°C. Solvent delay is 3 min. Mass spectral mass scan range 35 to 650 amu. Mass spectral identification of the compounds was performed in library NIST 05a. The temperatures at the GC and MS interfaces are 240°C and 280°C.
1.2.3 Determination of sample
In this experiment, semi-quantitative determination method was used and 2-methyl-3-heptanone was used as the internal standard. Quantitative determination of the detected substances was performed. The semi-quantitative determination method did not completely show the exact content in the soy sauce. It can be shown that under the same conditions, the content of a component between the sample and the control sample changes.
2. Results and discussion
2.1 Effect of soy sauce yeast on the overall aroma of soy sauce
The soy sauce aroma of each plant, due to the different ratio of raw materials, fermentation process, and local flora, has more or less certain differences. In terms of flavor composition, different raw material ratios, fermentation processes, and local climate will give their soy sauce The aroma composition of the product has a certain influence [10]. Table 1 shows the number of main aroma-type substances detected in the soy sauce yeast samples (Lushner's yeast and Qiuyao yeast) in each soy sauce factory sample.
Table 1. Comparison of the number of aromas before and after adding soy sauce yeast
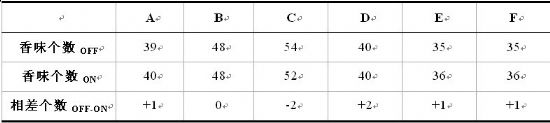
OFF: Soy sauce is made without Ang soy sauce yeast; ON: Soy sauce is made with chia soy sauce yeast
Individual substances are detected independently in OFF and ON, so the number of flavors is the same, but there are also differences, for example, the D plant.
Table 1 shows that before and after soy sauce yeast was added, the composition of the aroma components in soy sauce did not change much. That is, after the addition of soy sauce yeast, there was no major change in the overall composition of the soy sauce aroma. Most ingredients can be preserved. Soy sauce can maintain its own flavor composition before and after adding soy sauce yeast. From the information provided by the six factories, the vast majority of factories think that their soy sauce aroma has improved to a certain extent and the trend is positive.
2.2 Effect of Soy Sauce Yeast on Ethanol Content in Soy Sauce
Table 2 shows the change in ethanol content of each soy sauce sample and control sample after the addition of yeast (Rhizopus yeast).
Table 2. Effect of adding Angel soy sauce yeast on the ethanol content of soy sauce
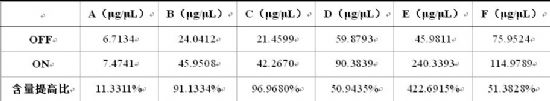
OFF: Soy sauce is made without Ang soy sauce yeast; ON: Soy sauce is made with chia soy sauce yeast
The data sheet in the table refers to the relative value of the sample. The final result shows the increase of ethanol in the soy sauce product.
Ethanol itself has an aromatic, irritating (pleasant) smell. Ethanol in soy sauce not only enriches the aroma of soy sauce, but also makes the mouth feel more mellow. The test results showed that in the soy sauce added with soy sauce yeast, the ethanol content has been improved to varying degrees. Due to the production process, production conditions, raw materials and other reasons, there is a significant difference in the increase, but it is certain that soy sauce Yeast has good ethanol production capacity during soy sauce brewing process. Manually adding (supplementing) soy sauce yeast during the soy sauce brewing process can increase the ethanol content in soy sauce. It is obtained from some soy sauce factories and soy sauce is added after soy sauce yeast is added. The speed of formation should be significantly increased. For the 90-day high-salt lean state process, some manufacturers reported that after adding soy sauce yeast, the soy sauce brewing time can be shortened by about 10 days without reducing (slightly improving) soy sauce quality.
2.3 Effect of Soy Sauce Yeast on the Content of 4-EP and 4-EG in Soy Sauce
4-Ethylguaiacol (4-EG) and 4-Ethylphenol (4-EP) are very important and representative aromatic compounds in soy sauce, and have a very important influence on the soy sauce. Tables 3 and 4 show the effect of the addition of soy sauce yeast (Qiaoqi Yeast) on these two substances.
Table 3. The effect of adding Angel soy sauce yeast on the content of 4-EG in soy sauce
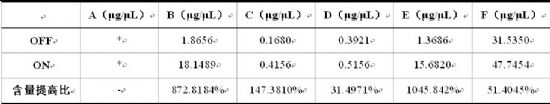
OFF: Soy sauce is made without Ang soy sauce yeast; ON: Soy sauce is made with chia soy sauce yeast
The data sheet in the table refers to the relative value of the sample. The final result shows the increase of 4-EG in the soy sauce product.
"*" indicates the trace amount of substance
Table 4. Effect of adding Angel soy sauce yeast on soy sauce 4-EP content
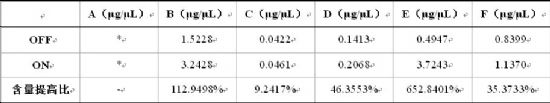
OFF: Soy sauce is made without Ang soy sauce yeast; ON: Soy sauce is made with chia soy sauce yeast
The data sheet in the table refers to the relative value of the sample, and the final result shows the increase of 4-EP in the soy sauce product.
"*" indicates a trace amount of substance, may not be added
China's soy sauce market has very distinct Chinese characteristics. The most intuitive thing is that the single-batch production cycle of Japanese-style soy sauce is about 6 months or even longer, and the vast majority of the production cycle of Chinese soy sauce will not exceed 4 months. The two substances, 4-EG and 4-EP, are mainly derived from the fermentation of ball-like yeast, which belongs to post-fermented yeast in the production of soy sauce. Due to the short post-fermentation time of most Chinese manufacturers, wild yeasts cannot rapidly synthesize 4-EG and 4-EP under natural conditions. Therefore, 4-EG and 4-EP in Chinese soy sauce are generally low, and The direct addition of ballistic yeast in soy sauce brewing can solve this problem very well. That is, the fermentation time can be shortened, the content of 4-EG and 4-EP can be relatively increased, and the quality of soy sauce can be ultimately improved.
2.4 Effect of Soy Sauce Yeast on the Content of 4-EP and 4-EG in Soy Sauce
In this test, objectively speaking, not all manufacturers have significantly improved the aforementioned substances after using soy sauce yeast. Table 5 shows the samples tested by each of these materials.
Table 5. Changes in related substances after adding Angel soy sauce yeast
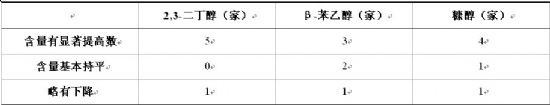
The comparison of the data is the comparison of soy sauce yeast added to each plant and soy sauce stuffed without soy sauce yeast.
The data shows that after adding soy sauce yeast, the content of most important yeast-related substances has been increased. It shows that in most manufacturers, Angel Soy Yeast has played its biological activity correctly, and has not changed a lot for the related substances of individual manufacturers. It may even cause a slight decrease. The main reasons may be raw materials, production processes and the correct use of yeast. .
3. Conclusion
From the results of this test, it can be seen that adding soy sauce yeast to the soy sauce brewing process does not have a negative effect on the main aroma of the soy sauce produced in each soy sauce producing area, and can basically maintain the unique aroma components of soy sauce. Secondly, after adding soy sauce yeast, the contents of various substances such as ethanol, 4-EG, 4-EP, and 2,3-dibutanol in soy sauce have been increased. These substances improve the aroma of soy sauce. The positive effect, in addition, such as sterols and other substances increase to a certain extent can also increase the mildew resistance of soy sauce. From this point of view, adding soy sauce yeast during soy sauce brewing is a good way to improve soy sauce quality.
Adding soy sauce yeast during soy sauce brewing can effectively improve the flavor of soy sauce and improve the quality of soy sauce. It has been recognized by soy sauce companies. At present, many soy sauce factories have established their own expansion yeast production process, adding yeast to their own soy sauce production process, in order to achieve the purpose of rapid flavoring of soy sauce. In addition, in order to adapt to the soy sauce production in the new situation, commercialized soy sauce dry yeast is now available, which not only facilitates the use of soy sauce factories, but also guarantees the quality of soy sauce yeast.
references
[1] Xu Qingping. Question and Answer on Soy Sauce Production Technology [M]. Beijing: China Textile Press, 2011, 1-26.
[2] Bao Qi'an. Soy Sauce Science and Brewing Technology [M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2011, 128-153.
[3] Lin Zushen. How to improve the flavor of soy sauce from the production process [J]. Brewing in China, 2010,
(9): 13-15.
[4] Catrinus van der Sluis, Johannes
Tramper, Rene H. Wijffels. Enhancing and accelerating flavour formation by salt-tolerant yeasts in Japanese soy-sauce processes[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2001, 12(9): 322-327.
[5] Lu Meihuan, Li Lijun, He Jianchao. Research progress of application of salt-tolerant ester-producing yeast in soy sauce production [J]. Chinese Flavoring, 2010, 35(10), 48-51.
[6] Chen Bin, Lu Wei, Wang Fujie. Analysis of Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Salt-tolerant Yeast for Soy Sauce Fermentation and Identification of Strain [J]. Brewing in China, 2010, (11), 42-45.
[7] Shigehiro Kataoka. Functional effects of Japanese style fermented soy sauce(Shoyu) and its components[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2005, 100(3): 227-234.
[8] Yan Yulin. Determination of soy sauce and balsamic vinegar and identification of production process [D]. Master thesis of Huazhong Agricultural University.
2008, 13-16.
[9] Makio Kobayashi, Satomi Hayashi.Supplementation of NaCl to starter culture of the soy yeast Zygosaccharomyces rouxii[J]. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 1998, 86(6): 642-644.
[10] Michael Jansen, Janine H. Veurink, Gert-Jan W. Euverink. Growth of the salt –tolerant yeast Zygosaccharomyces rouxii in microtiter plates: effects of NaCl, PH and temperature on growth and fusel alcohol production from branched-chain amino acids [J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2003, 3(3): 313-318.
The application effect of active dry soy sauce yeast in soy sauce production
LEI Jin-cheng1, CHANG Xu1, SONG Huan-lu2, XU Qian-qian2
(1. Brewing & Bioenergy Research Institution, Brewing & Bioenergy Business Unit, Angel Yeast Co., Ltd, Yichang 443003, China 2. College of Chemical & Environmental Engineering, Beijing Technology & Business University, Beijing 100048, China)
Abstract:
The Head-Space Solid-phase micro-extraction (HS-SPME) and capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) was used to determinate aroma components in soy sauce. The application effect of soy sauce yeast in soy sauce production was discussed, Especially in main effect of alcohol, Phenol, 4-ethyl-2-methoxy-(4-EG), Phenol, 4-ethyl-(4-EP), etc. The
Test result shows adding active dry soy sauce yeast can improve the quality of soy sauce.
Keywords:soy sauce production, soy sauce yeast, HS-SPME, GS-MS, aroma improvement
Kitchen faucet. Installed on the kitchen sink, used to put cold water, hot water or a mixture of hot and cold water. Its structure includes: screw lift type, metal ball valve type, ceramic spool type, etc. The valve body is made of brass, chrome-plated, gold-plated and various metal lacquers. The shape is various, the handle has a single, double handle of the points.
Kitchen Taps,Delta Kitchen Faucets,Kitchen Sink Faucets,Sink Tap
Kaiping Jianfa Sanitary Ware Co.,Ltd. , https://www.jfsanitary.com