Recently, the research team led by Prof. Wu Ziyu from the China Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory and the team led by Chen Xianhui used X-ray absorption spectroscopy to study the isotope effect of iron-based superconducting materials on the three-dimensional atomic scale and made important progress. This result was published on the April 29th Nature Scientific Group (Scientific Reports) of Nature Publishing Group (NPG).
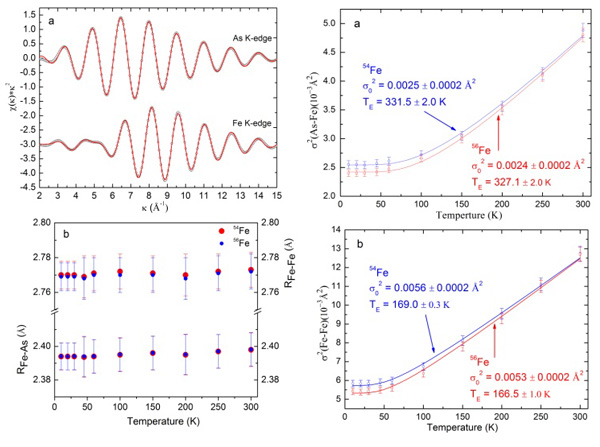
Since the discovery of iron-based superconducting materials in 2008, it has been one of the important research hotspots for condensed matter physics. However, there is widespread controversy over the understanding of iron-based superconducting mechanisms. Following the discovery of the isotope effects of iron-based superconducting materials using Tc and magnetic measurements for the first time, Professor Chen Xianhui of the school and Wu Ziyu’s research group [Nature 459, 64-67 (2009)] used temperature of newly developed isotope microscopic effects. Depending on the EXAFS detection method, the microscopic mechanism of the isotope effect of iron-based superconducting materials was studied. The latest research points out that for ![]() Superconductors and isotope doping have little effect on the average health and static distribution of Fe-As and Fe-Fe, but modulate their thermal disorder distribution; Fe-As of different iron isotope samples can be accurately obtained through correlation with Einstein model. With the characteristic frequency of Fe-Fe, the isotopic effect factors of the local lattice vibration of Fe-As and Fe-Fe were measured. The isotope effect factor measured by this microscopic method is basically the same as the isotope index measured by resistance and magnetic susceptibility, further indicating that the electro-phonon interaction is
Superconductors and isotope doping have little effect on the average health and static distribution of Fe-As and Fe-Fe, but modulate their thermal disorder distribution; Fe-As of different iron isotope samples can be accurately obtained through correlation with Einstein model. With the characteristic frequency of Fe-Fe, the isotopic effect factors of the local lattice vibration of Fe-As and Fe-Fe were measured. The isotope effect factor measured by this microscopic method is basically the same as the isotope index measured by resistance and magnetic susceptibility, further indicating that the electro-phonon interaction is ![]() The superconducting mechanism plays an important role. At the same time, the Fe-Fe and Fe-As vibrations are distributed in different vertical planes. They have almost equivalent isotope effects, indicating that
The superconducting mechanism plays an important role. At the same time, the Fe-Fe and Fe-As vibrations are distributed in different vertical planes. They have almost equivalent isotope effects, indicating that ![]() Has three-dimensional superconducting properties that are different from copper-based high-temperature superconducting materials.
Has three-dimensional superconducting properties that are different from copper-based high-temperature superconducting materials.
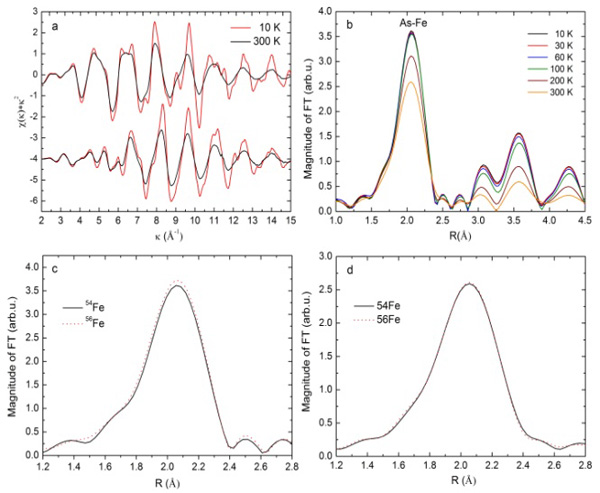

The synchrotron radiation source has excellent characteristics such as high resolution, high monochromaticity, strong penetrability, and wide spectrum, and has become an important platform for cutting-edge scientific research. A series of new methods and technologies based on synchrotron radiation devices developed by the Wuziyu research group can be used to study the microlocal electronic/atomic structures of superconducting materials, magnetic materials, and various low-dimensional materials.
This project was supported by the Knowledge Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
The utility model provides an electronic igniter, which is characterized in that it is composed of a shell with an ignition port at the left end and a button port on it, an ignition tube connected with the ignition port at the left end of the shell, an ignition device fixedly connected with the button port, and a cable connected with the ignition device. The ignition device is composed of a rectangular shell and a button sliding connected with the upper end of the shell, The utility model is composed of a striker connected with the lower surface of the button, a power generation ceramic block fixedly connected with the bottom of the shell, a thimble connected with the upper surface of the power generation ceramic block, and a spring which is connected with the power generation ceramic block and sheathed outside the thimble. The electronic igniter has the characteristics of simple structure, safe and reliable, convenient operation, no need to use batteries, etc., which is not only economical and environmental protection, but also convenient for wide promotion.
Jet Flame Camping BBQ Outdoor Lighter,Outdoor Gas Lighter Torch,Refillable BBQ Gas Lighter
Shangqiu Zhengtu Hardware Technology Co,.Ltd , https://www.zlztlighter.com