With the continuous consumption of global energy, traditional energy sources will also be depleted in the near future. Countries have begun to pay attention to the development and utilization of new energy since the 1990s.
Our government is also actively developing new energy sources. On March 9, 2015, the Energy Bureau announced the statistics of photovoltaic power generation in 2014. The cumulative installed capacity of photovoltaic power generation was 28.05 million kilowatts, including 23.38 million kilowatts of photovoltaic power stations and 4.67 million kilowatts of distributed power.
However, at present, the system efficiency of photovoltaic power plants is not very high. Irrational design and immature technology are the reasons that lead to low overall efficiency of power plants.
This article discusses how to increase plant efficiency in the design process from the design aspect.
First of all, what are the losses of photovoltaic power plants? Currently known are the cosine loss of components, the array loss of components, the loss of inverter efficiency, the loss of cable consumption, and the loss caused by environmental impact.
Since we talk about the loss, can we reduce such losses in the process of our design?
Below we discuss the cosine loss of components to explore how to reduce such losses.
The so-called cosine loss can also be called the cosine effect is the cosine relationship of solar radiation angle with the sun, say white is the air mass AM (Air Mass), we usually use the standard spectrum when estimating the photovoltaic power generation system power generation, such as AM1 .5, but actually the solar radiation energy density is different in different regions.
For example, in the same sunlight, different solar radiation angles receive different radiation energy densities.
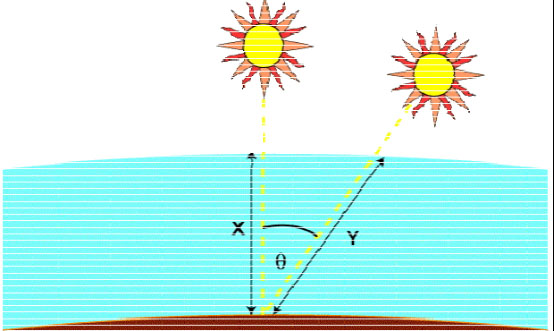
As shown in the above figure, the air quality is defined as:
Where θ is the zenith angle (the angle between the incident ray and the direction of the local zenith), vertical irradiation of sunlight at any time of the day can be described by atmospheric quality.
Those who work in the photovoltaic power plant industry know that our components must be laid at the best angle when laying. It is also known that the power plant with the best tilt angle is the highest. However, many people only know about it.
Here we discuss and discuss together in this regard.
In fact, the most fundamental purpose of laying our way to the Olympic dip is to reduce the incident angle of light. Since the earth we live in is a sphere, the sun's rays are illuminated by parallel rays of light that form a certain angle with the surface of the earth. Due to the optical properties, light refracts and reflects when it strikes an object.
Most of the current components used in power stations use tempered glass. When the light is perpendicularly incident, the amount of reflected light is the smallest, that is, the silicon wafer under the tempered glass absorbs the most light, so the amount of electricity generated is also the most. The larger the incident angle, the smaller the incident amount of light.
According to the experimental time, it has been proved that when the incident angle is less than 45°, the light passing rate can reach more than 93%. When the incident angle is greater than 45°, the light passing rate will be significantly reduced. The purpose of our design is to use dips to lay the light as small as possible so as to reduce losses.
As technology advances, our design should also improve. Only better communication can improve the design of the power station. These are some of my personal experiences in the design process.
Creative Night Light, Best Corded Night Light, Night Light for Christmas
Ningbo Deamak Star Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.deamakstar.com