Recently, Tang Yongbing (corresponding author), a researcher of the Functional Thin Film Materials Research Center of the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and his team members have made new progress in flexible sodium-based dual ion batteries. Related research results "A Flexible Dual-Ion Battery Based on Sodium-Ion Quasi-Solid-State Electrolyte with Long Cycling Life" have been published online in the materials field journal Advanced Functional Materials ("Advanced Functional Materials", Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019 , 1906770).
Sodium-based dual-ion batteries (SDIBs) combine the combined advantages of sodium-ion and dual-ion batteries, and have the advantages of high operating voltage, environmental protection, and low cost. However, the reported SDIBs generally use traditional liquid ester solvents as electrolytes, which makes the battery prone to decomposition under high operating voltage. In addition, the solvent molecules of the traditional liquid electrolyte system and the graphite positive electrode are prone to co-intercalation, which causes the graphite positive electrode to peel off during the cycle. Therefore, the cycle performance of SDIBs based on liquid electrolyte still needs to be further optimized.
To solve the above problems, Tang Yongbing team members Xie Donghao, Zhang Miao, Wu Yue and others developed a quasi-solid electrolyte (QSSE) with a three-dimensional cross-linked structure. At high voltages, the electrolyte has more stable cycling characteristics than traditional liquid electrolytes, and the three-dimensional polymer skeleton also helps relieve the volume expansion stress of the electrode material. These QSSE-based SDIBs show excellent cycle stability, and the capacity retention rate is 97.5% after 600 cycles at 5C rate, which is the best performance reported in SDIBs. In addition, the battery has excellent flexibility and wide temperature range performance (-20-70 degrees), and has good application prospects in high-performance flexible energy storage and other fields.
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangdong Province and Shenzhen Science and Technology Projects.
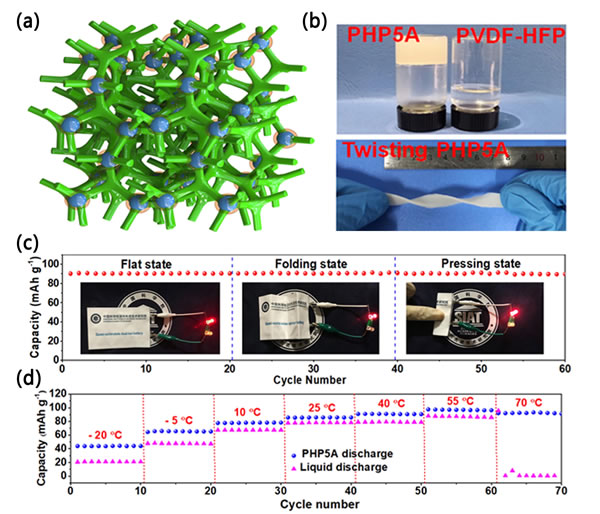
Figure (a). 3D schematic diagram of a quasi-solid polymer formed by the Lewis acid-base intermolecular bonding between PVDF-HFP and Al2O3 nanoparticles; (b) Comparative photographs of quasi-solid electrolyte and liquid electrolyte (top) , Optical photo of quasi-solid electrolyte torsion experiment (below); (c) Cyclic curve of flexible SDIB in flat, folded and squeezed state; (d) Based on quasi-solid electrolyte and liquid electrolysis Liquid circulation performance comparison.
Heat Lamp Oval Marble Carving Station,Oval Marble Carving Station,4-Lamp Carving Station,Marble Culinary Station
Shaoxing Biaoyi Hardware Products Co., Ltd. , https://www.byeob.com